food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome in adults
Diarrhea that begins after vomiting. Annals of Allergy Asthma.

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food protein.

. Most of the reactions were due to seafood mollusks crustaceans and fish and egg but other foods like peanut almond mushroom corn chicken and duck were also implicated. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon but serious disorder and has been defined as affecting infants with onset in the first year of life 1. Cows milk and soy are the most frequent causative foods and the natural history is usually one of spontaneous resolution in childhood 2.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract mainly in infants and young children. A majority of cases occur during infancy particularly. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES.
FPIES can occur in adults although this is uncommon. In fact FPIES CAN present in adults of any age though the current research suggests it occurs in adults less frequently than in children. FPIES symptoms can be very serious and can include turning grey or blue dehydration and even going into shock.
Epub 2012 Jul 24. Food-protein induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated reaction affecting predominantly infants and children. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is increasingly recognized in adults with a predominance in women. Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and usually occur 2-3 hours after eating a food. PDF Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy commonly diagnosed in infants and young children.
Symptoms of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can vary from child to child and in severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. FPIES presents in two different forms.
Changes in blood pressure and body temperature. While the pathophysiology of FPIES is poorly understood the clinical presentation of acute FPEIS reactions has been well characterized. FPIES usually develops in infancy and resolves around 3-5 years of age.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy typically. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea. 1 2 This syndrome is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food.
In its acute form FPIES presents with vomiting that usually begins 1 to 4 hours after trigger food ingestion. Many allergists report that symptoms suggestive of FPIES are on occasion reported by adult patients and mainly refer to ingestion of seafood. This syndrome typically occurs in infants and the typical culprit foods for children are cows milkdairy soy rice and oat.
In some cases symptoms can progress to dehydration and shock brought on by low blood pressure and poor blood circulation. Differences in clinical manifestations trigger foods and prognosis compared to pediatric FPIES have been reported. The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines.
In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES has been categorized into acute and chronic forms. From a diagnosis that did not exist to a condition in need of answers.
I agree with you that this is likely adult-onset food protein induced enterocolitis FPIES a non-IgE dependent immune response to food. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults. Vomiting is often followed by a paleness to the skin.
Adult cases have been recently reported but are rare 1. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a delayed non-IgE mediated gut allergic reaction to a food s usually presenting in the first two years of life with an estimated incidence in this age group of 1 in 7000 children. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a nonIgE-mediated food allergic disorder that can manifest with symptoms of projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and may be accompanied by lethargy hypotonia hypotension hypothermia and metabolic derangements. The evolution of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome.
A similar syndrome in adults has been associated primarily with. FPIES food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome is a serious allergic reaction to certain foods. That said this diagnosis demands age-appropriate resources for.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon. An acute form and a chronic form. 1 FPIES usually starts in infancy although onset at older ages is.
3 Diagnosis of FPIES is difficult. Vomiting typically occurring two hours after ingestion. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy that presents with delayed vomiting after ingestion primarily in infants.
There is certainly crossover in the usefulness of FPIES resources for all ages. Bryan N Fernandes Robert J Boyle Claudia Gore Angela Simpson Adnan Custovic. Adult Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Introduction.
Avoidance of triggering foods ensuring good nutrition healing the gut balancing the immune system and maintaining a good inflammatory balance are keys to treatment.
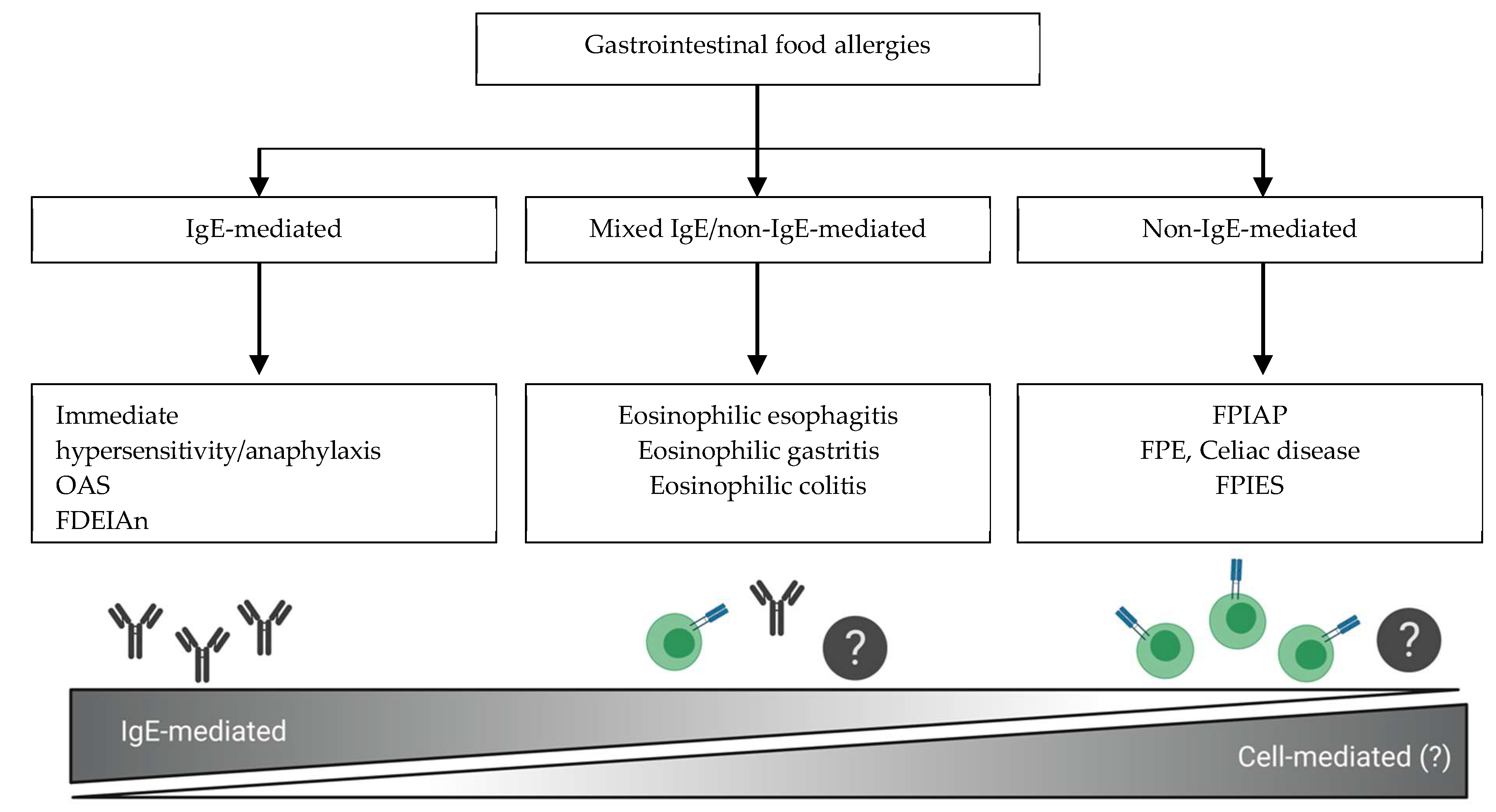
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

Study Characterizes Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome In Adults

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

International Fpies Association Facebook

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Nutrients Free Full Text Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome In Children With Down Syndrome A Pilot Case Control Study Html

International Fpies Association Facebook

Fpies In Babies Symptoms Risk Factors And More

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis
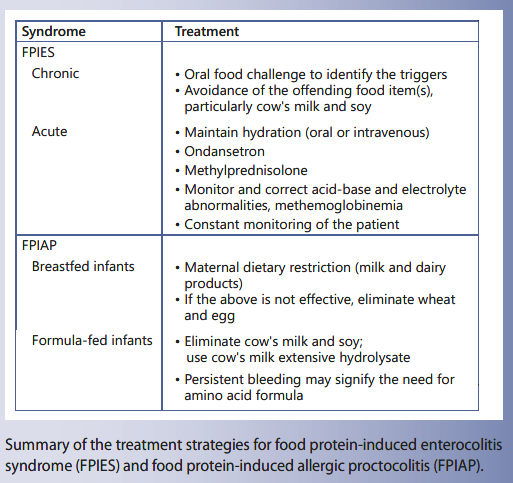
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome As A Cause For Infant Hypotension The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine
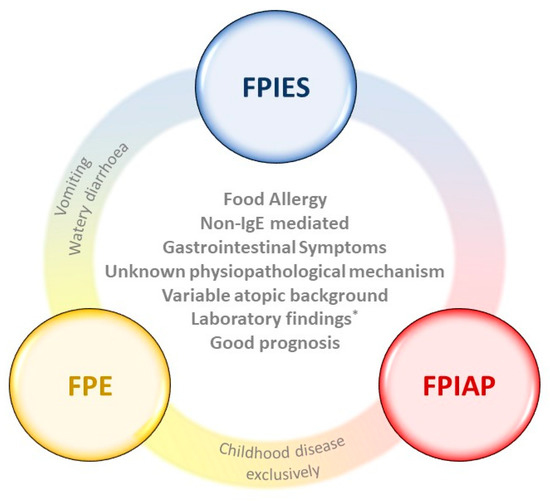
Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology